The SA 537 Carbon Steel Class 1 Plates market represents a critical segment within the global steel industry, characterized by robust growth projections and increasing demand across multiple industrial sectors. This comprehensive analysis reveals that the carbon steel plates market is valued at USD 1,019.86 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 1,514 billion by 2034, exhibiting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.03%.
The pressure vessel steel plates segment specifically is experiencing even more dynamic growth, with market valuations expected to increase from USD 10.2 billion in 2024 to USD 15.6 billion by 2032, reflecting a CAGR of 4.8%.

Technical Specifications and Properties
Chemical Composition and Material Characteristics
ASME SA 537 Class 1 Plates represent a specialized grade of heat-treated carbon-manganese-silicon steel plates designed specifically for fusion welded pressure vessels and structural applications. These plates exhibit superior mechanical properties compared to standard ASTM A516 grades, making them the preferred choice for demanding industrial applications. The chemical composition includes carbon content limited to 0.24% maximum, manganese ranging from 0.70-1.35% for plates ≤40mm thickness and 1.00-1.60% for thicker plates, silicon content between 0.15-0.50%, and controlled levels of phosphorus and sulfur at 0.025% maximum each.
The material’s normalized sa 537 plate condition provides enhanced yield strength of 345 MPa (50 ksi) for plates up to 65mm thickness, while maintaining tensile strength between 485-620 MPa (70-90 ksi). This combination of properties ensures exceptional performance in high-pressure environments while maintaining excellent notch toughness characteristics essential for low-temperature service applications.
Mechanical Properties and Performance Standards
The mechanical properties of sa 537 cl 1 plates distinguish them from conventional carbon steel grades through their superior strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced ductility. These plates demonstrate minimum elongation values of 22% in 50mm gauge length and 18% in 200mm gauge length, indicating excellent formability characteristics. The normalized heat treatment process refines the grain structure, resulting in improved mechanical properties throughout the cross-section while maintaining consistent performance across varying plate thicknesses.

The sa 537 cl 1 equivalent material’s excellent low-temperature toughness makes it particularly suitable for applications requiring Charpy V-notch impact testing, with typical requirements of 30 ft-lbs (41 J) at -40°F (-40°C) in longitudinal specimens. This performance characteristic ensures reliable operation in arctic conditions and cryogenic applications where conventional carbon steels might exhibit brittle fracture tendencies.
Manufacturing Process and Production Techniques
Steel Making and Primary Processing
Iron Smelting and Refinement
The manufacturing process of ASME SA 537 plates begins with iron smelting. Iron ore is extracted and refined in blast furnaces along with coke, limestone, and other raw materials. Next, the molten iron undergoes converter steelmaking. Oxygen is blown into the molten iron to oxidize and remove impurities such as carbon, silicon, manganese, and phosphorus. As a result, this process generates significant heat, raising temperatures to about 1,600°C. It effectively eliminates impurities without requiring additional fuel.
Elemental Control and Quality Assurance
As a normalized SA 537 plate supplier in India, manufacturers focus on precise elemental control to achieve the chemical composition specified in ASTM A537 standards. Throughout this phase, quality control measures include continuous spectroscopic analysis of the chemical composition. Therefore, all elements remain within the specified tolerances, ensuring consistency and reliability.
Hot Rolling and Forming Operations
Rolling Process and Dimensional Accuracy
The rolling process is a critical stage in SA 537 Class 1 plate production. Steel slabs are heated to temperatures between 1,100°C and 1,250°C, then passed through a series of rolling mills to achieve the desired dimensions. In particular, 4-high reversible finishing mills with maximum loads of 7,000 tons minimize internal defects in thick plates. Moreover, automatic gauge and shape control systems maintain dimensional accuracy throughout production.
Advanced Cooling Technologies
Modern plate rolling facilities employ advanced technologies such as PILAC (POSCO In-line Accelerated Cooling) systems. These systems enable the production of high-strength steel without additional heat treatment through controlled rolling and accelerated cooling. Additionally, mist cooling methods with suction-type systems provide high cooling capacity while maintaining uniform temperature gradients across the plate width. Consequently, quality deviations are reduced significantly.
Normalization Heat Treatment Process
Standard Normalization Technique
SA 537 Class 1 plates undergo normalization heat treatment to refine their structure. In this process, the plates are heated above the critical transformation temperature (Ac3), typically around 900–950°C, followed by air cooling. This step refines the grain structure, producing fine ferrite grains that enhance strength and toughness.
Normalizing Rolling Technique
The normalizing rolling technique represents a more advanced manufacturing approach. Here, the final deformation occurs within the normalizing temperature range, eliminating the need for a separate heat treatment. Therefore, manufacturers achieve equivalent metallurgical properties while reducing production time and costs. At the same time, this method ensures compliance with the mechanical properties specified in ASTM A537 Class 1 standards.
Market Analysis and Growth Projections
Global Market Size and Regional Distribution
The global carbon steel plates market demonstrates robust growth trajectories across all major geographic regions, with Asia-Pacific leading both production and consumption patterns. The region accounts for over 66% of global market share in 2026, driven by rapid industrialization and construction activities in countries like China and India. North America represents approximately 20% of the market share, supported by significant demand from automotive, defense, and infrastructure sectors, while Europe contributes around 15% of the global market.
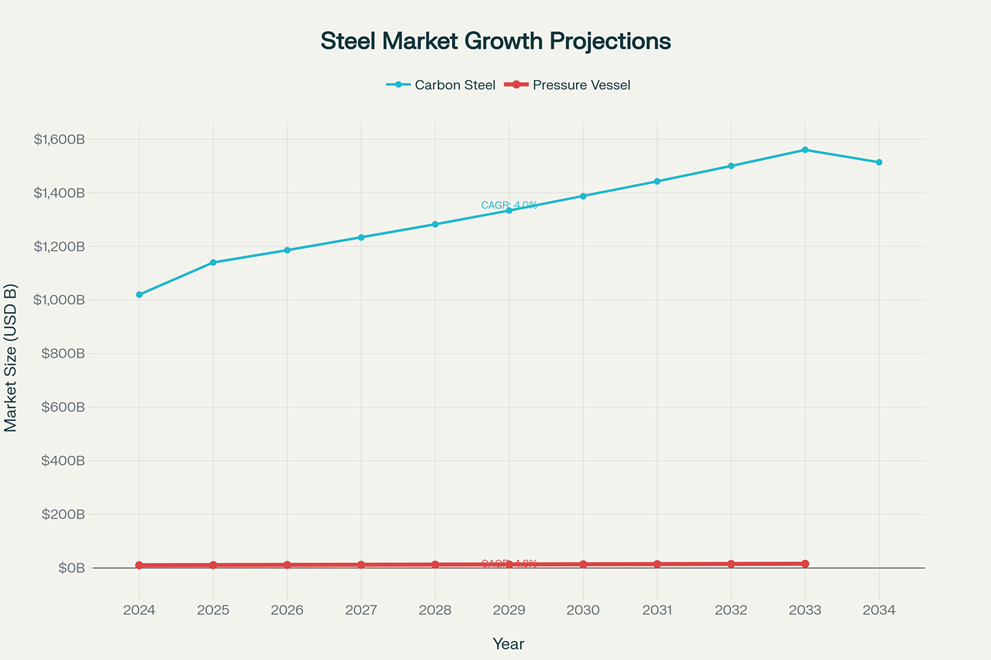
Market research indicates that the steel plate industry is experiencing steady expansion, with global valuations increasing from USD 65.24 billion in 2024 to a projected USD 96.79 billion by 2030, representing a CAGR of 3.22%. The pressure vessel quality (PVQ) steel plates segment, which includes SA 537 grades, shows even stronger growth momentum with market values expected to reach USD 2.32 billion by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 8.6%.
Industry Drivers and Market Dynamics
Several key factors drive the sustained growth in the SA 537 Carbon Steel Class 1 plates market, with construction industry expansion serving as the primary catalyst. To begin with, the global construction industry, valued at approximately USD 12 trillion in 2024, represents around 6% of global GDP. As a result, it directly drives demand for high-quality steel plates in bridge construction, high-rise buildings, and infrastructure projects.
In addition, the energy sector—particularly oil and gas exploration—provides significant market momentum. The increasing demand for pressure vessels used in exploration, extraction, and processing activities continues to rise. Moreover, advanced extraction technologies such as hydraulic fracturing require high-quality pressure vessel steel plates capable of withstanding extreme pressures and temperatures. This trend further supports overall market growth.
Furthermore, chemical and petrochemical industries contribute substantially to market expansion. Their reliance on pressure vessels for storage and transportation of hazardous materials is growing rapidly. At the same time, the rising emphasis on safety regulations and the need for reliable materials in chemical processing plants further drives demand for specialized steel plates like SA 537 Class 1.
Industrial Applications and End-User Industries
Pressure Vessel and Boiler Construction
Oil and Gas Sector
SA 537 Class 1 plates are widely used in pressure vessel construction. Their strength and toughness ensure safe containment of high-pressure fluids and gases. These plates are essential in the oil and gas industry, supporting production and refining operations. They are commonly used in the manufacturing of petroleum products such as gasoline, diesel fuel, and lubricants.
Power Generation Industry
Power plants represent another major application area. SA 537 Class 1 plates are used in components such as superheaters, reheaters, and evaporators. Their ability to withstand extreme temperatures and pressures, combined with excellent mechanical properties, makes them ideal for critical power infrastructure.
Chemical Processing and Petrochemical Industries
Chemical Processing Equipment
In chemical processing, SA 537 Class 1 plates perform well in harsh environments involving chlorine, hydrogen sulfide, and sulfur dioxide. Their corrosion resistance and durability make them suitable for chlorine storage tanks and other demanding applications where conventional materials may fail.
Petrochemical Applications
The petrochemical industry uses these plates in reactors and processing equipment exposed to corrosive and high-stress conditions. Heat-treated variants such as SA 537 Class 2 offer even higher tensile and yield strength than ASME SA516 grades. This makes them indispensable for critical petrochemical processes.
Military and Defense Applications
Armored Vehicles and Equipment
SA 537 Class 1 plates play a vital role in defense manufacturing. They are used in military-grade tanks and transporters that must endure harsh weather and combat conditions. Their toughness and durability ensure reliable performance in extreme environments.
Aerospace and Defense Sectors
The aerospace industry also relies on these plates for specialized defense equipment. Lightweight yet strong pressure vessel materials are essential for high-performance applications under extreme conditions. SA 537 Class 1 plates maintain structural integrity under stress, making them valuable in advanced defense manufacturing.
International Standards and Global Equivalents
Worldwide Equivalent Grades and Standards of SA 537 Class 1 Plates
SA 537 Class 1 plates conform to multiple international standards, facilitating global trade and ensuring interchangeability across different markets. The primary equivalent grades include German DIN standard 19Mn5, European EN standard P355GH, Japanese JIS standard SPV36, British BS standard 224Gr.490, and French AFNOR standard A52CP. These equivalent standards ensure that SA 537 Class 1 plates can be specified and utilized in international projects while maintaining consistent performance characteristics.
The material’s versatility across international standards reflects its widespread acceptance in global engineering applications. Italian UNI standard Fe510-1KW, Spanish UNE standard A52RCI, Swedish SS standard 2103, and Finnish SFS standard Fe52BP all provide equivalent specifications, demonstrating the material’s universal applicability in pressure vessel construction.
Compliance and Certification Requirements
SA 537 Class 1 plates must undergo comprehensive testing and certification processes to ensure compliance with international quality standards. These requirements include chemical composition analysis, material grain size determination, mechanical testing including tensile and Charpy impact tests, and ultrasonic examination for internal defect detection. Third-party inspection agencies such as CE, DNV, KR, TUV, RINA, CCS, GL, LR, and ABS provide independent verification of material properties and manufacturing quality.
Quality assurance protocols encompass destructive and non-destructive testing methods, including hardness testing, pitting resistance evaluation, macro-micro inspections, flattening-flaring assessments, and radiographic scrutiny. These comprehensive quality control measures ensure that SA 537 Class 1 plates meet the stringent requirements of pressure vessel applications while maintaining consistent performance across different production batches.
Global Manufacturers, Suppliers, and Market Players
Major International SA 537 Carbon Steel Class 1 Plates Manufacturers
The global SA 537 Class 1 plates market features several prominent manufacturers and suppliers serving international markets. Major players collectively account for approximately 29% of global tonnage production and maintain extensive distribution networks spanning multiple continents.
Asian manufacturers dominate the global market in leading production of SA537 Cl 1.
Regional SA 537 Carbon Steel Class 1 Plates Suppliers and Stockists
Indian sa537-1 plate manufacturers and suppliers play crucial roles in the global sa537 class 1 steel market, with companies like Chiranjiv Steel Centre serving as major stockists and exporters. These companies maintain comprehensive inventories and provide customized solutions for diverse industrial applications across international markets.
Regional distributors extend market reach through established networks in key industrial regions. We also maintain strategic locations in major industrial centers, ensuring reliable supply chains for SA 537 Class 1 plates. These distributors provide value-added services including cutting, machining, heat treatment, and quality testing to meet specific customer requirements.
Export Markets and Global Distribution of SA 537 Cl 1 material
SA 537 Carbon Steel Class 1 Plates enjoy widespread global distribution, with major export markets including Azerbaijan, Brazil, Ghana, Kenya, Algeria, Angola, South Africa, Argentina, Zambia, Colombia, Uganda, Taiwan, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Qatar, Oman, Kuwait, Iraq, Egypt, Israel, Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, Thailand, Philippines, and Kazakhstan.
This extensive geographic coverage reflects the material’s universal acceptance in international pressure vessel construction projects.
The global supply chain encompasses multiple distribution channels, from direct mill shipments to regional stockist networks, ensuring reliable material availability for time-sensitive projects. Exporters maintain comprehensive quality documentation and certification packages to facilitate international trade while ensuring compliance with destination country standards and regulations.
Future Market Trends and Technological Innovations
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Decarbonization Initiatives by Major Producers
The carbon steel plates industry is shifting strongly toward sustainability and environmental responsibility. Major steel producers are investing heavily in decarbonization technologies. Between 2018 and 2024, companies aim to cut absolute scope 1 and 2 emissions by 46%. This is being achieved through higher electric arc furnace (EAF) steel production and more than USD 1 billion in strategic decarbonization projects.
Hydrogen-Based Green Steel Projects
Green steel production is revolutionizing manufacturing processes. H2 Green Steel in Sweden is building a €6.5 billion plant designed to reduce carbon emissions by 95%. This breakthrough will replace coking coal with hydrogen, making steel production significantly cleaner.
Electra’s Low-Temperature Steelmaking
Electra has developed a new production method that operates at much lower temperatures. It uses chemical solutions and electricity instead of traditional methods. This innovation substantially reduces both energy consumption and overall emissions.
Technological Advancements and Industry 4.0 Integration
AI and Automation in Steel Manufacturing
Artificial intelligence and automation technologies are transforming SA 537 Class 1 plate production. AI systems improve process efficiency and quality assurance. They also optimize energy usage by adjusting heating and cooling intelligently.
Computer Vision for Defect Detection
Computer vision techniques are enhancing inspection processes. High-resolution cameras and sensors capture detailed surface images. Algorithms then analyze these images to identify imperfections more accurately than manual inspections.
Thermo-Mechanical Controlled Processing (TMCP)
Advanced manufacturing methods such as Thermo-Mechanical Controlled Processing (TMCP) combine controlled rolling and rapid cooling. This delivers higher strength and toughness while lowering energy use. TMCP supports decarbonization targets and helps reduce production costs.
Market Outlook for SA 537 Class 1 Plates
The market outlook for SA 537 Carbon Steel Class 1 Plates remains strong. Demand is supported by industrial expansion, infrastructure projects, and technological innovation. As safety regulations and environmental requirements grow stricter worldwide, the need for high-quality, certified pressure vessel materials will continue to rise. This trend ensures sustained growth for SA 537 Class 1 plates across global markets.
